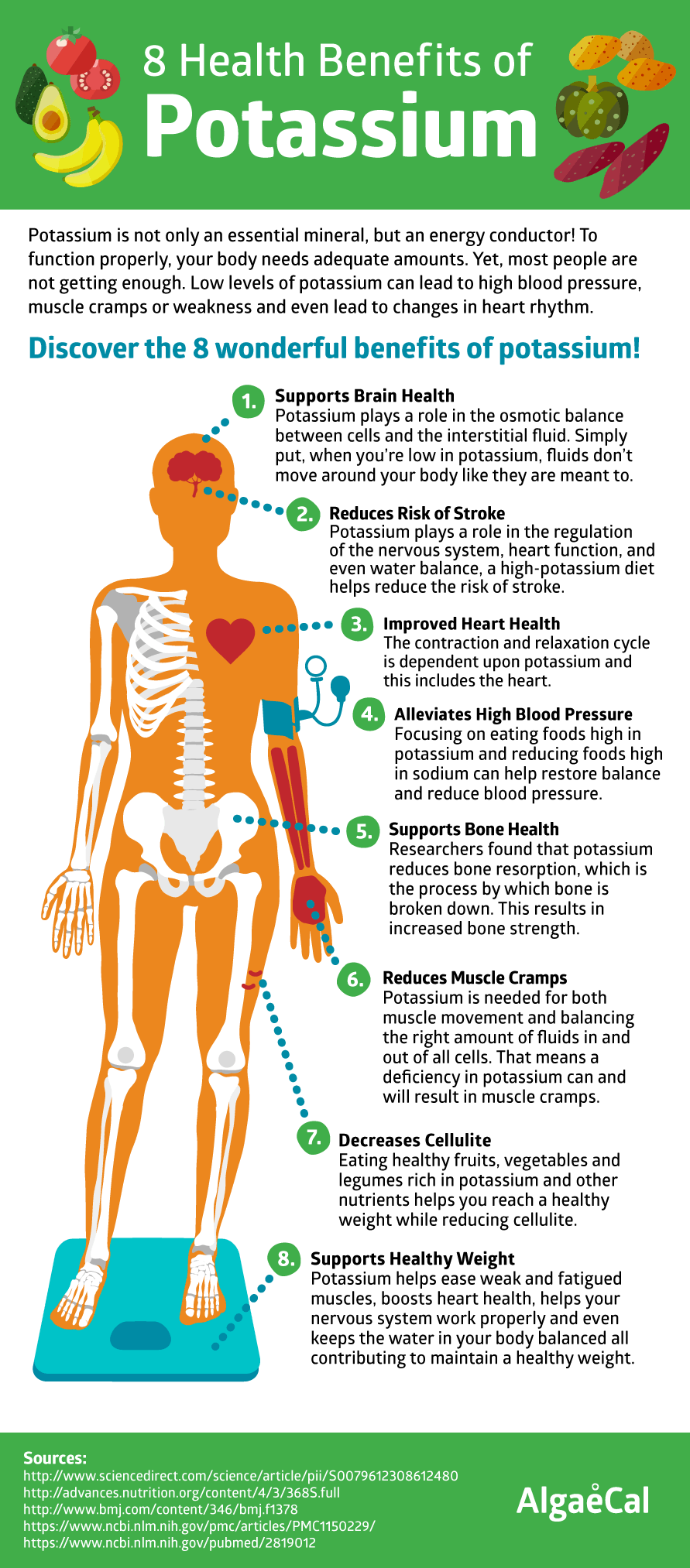
What Is the Purpose of Potassium in the Human Body?
Potassium is one of the most important electrolytes in the human body, with others including chloride, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and sodium. As an electrolyte, potassium is vital to the healthy functioning of all of your body’s cells, tissues and organs.
According to the National Academies’ Food and Nutrition Board, an adequate intake of potassium is 4.7 grams per day. In North America, however, the average man consumes approximately 3 grams and the average woman less than 2.5 grams of potassium per day. As such, most people can benefit from increasing their daily potassium intake. Particularly good sources include bananas, citrus juices, avocados, tomatoes, potatoes, lima beans, salmon, cod, chicken and most meats.
Electrolyte
Electrolytes are substances that help conduct electricity in your body. Potassium is one of the most important electrolytes in the human body, with others including chloride, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and sodium. As an electrolyte, potassium is vital to the healthy functioning of all of your body’s cells, tissues and organs. It also helps to control the amount of water in your body and maintain a healthy blood pH level. As you lose electrolytes in your sweat, you should always obtain a source of these important minerals during or after a bout of intense physical activity.
Blood Pressure
A balance of sodium and potassium is important for your body’s electrolyte functions. As your body works hard to maintain this balance, you can reduce the impact of a high sodium intake by consuming more potassium. Because of sodium’s impact on your blood pressure, a boost in your daily potassium intake can help you to maintain a healthy blood pressure or lower it to healthy levels. However, you cannot rely entirely on sodium and potassium to lower your blood pressure. In addition to obtaining regular exercise, your intake of fats, salt, cholesterol, protein, fiber, calcium and magnesium can also impact your blood pressure.
Muscular Function
Potassium is particularly important for the ability of your skeletal and smooth muscles to contract. Because of this, an adequate intake of potassium is important for regular digestive and muscular functioning. Potassium is also vital to the health of your heart, as a normal heart rhythm arises from optimal muscular functioning. This is especially apparent if you have excessively high or low potassium levels, both of which can cause an irregular heartbeat. As heart arrhythmias are potentially life-threatening, you should always maintain an adequate daily intake of potassium.
High or Low Intakes
Your body easily excretes excess potassium in your urine. Because of this, the National Academies do not publish recommendations for your maximum daily potassium intake. If you have damaged or impaired kidneys, however, you should not have more than 4.7 grams of potassium per day to avoid developing an irregular heartbeat. You should also be careful not to have too little potassium. A moderate potassium deficiency can increase your blood pressure, lead to salt sensitivity, increase your risk of cardiovascular disease and reduce the health of your bones. In addition to heart arrhythmias, excessively low potassium levels — a condition called hypokalemia — can cause glucose intolerance, weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps and stomach problems.
Source: Healthy Eating